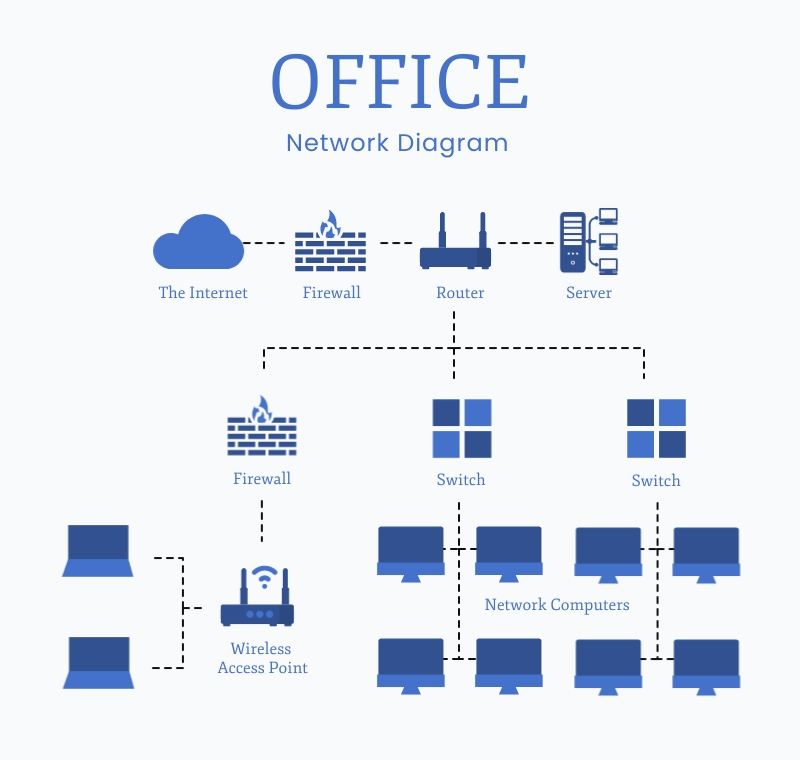
What is Office Network?
Office networks are computer networks specifically designed to handle the needs of business operations. They provide a platform for various workplace applications such as word processing, spreadsheet programs, and database management systems as well as networking communication protocols for inter-office communications and collaborations.
Office networks generally use Ethernet technology to provide reliable connections between computers, printers, and other equipment. These networks also provide secure access to the Internet and other remote resources.
Additionally, office networks often employ virtual private networks (VPNs) for secure data transfers over public or unsecured Wi-Fi connections.
What Do You Need To Set Up Office Network?
To set up an office network, you’ll need a few basic components. These include:
Network Hardware Requirements
- ISP Lease Line Connection: An ISP lease line connection provides a direct connection to the internet and is required for large office networks.
- Router: A router serves as the gateway to the outside internet, allowing traffic from different devices on your office network to flow in and out. It also helps manage data traffic within your office network.
- Switches: Switches facilitate communication between computers, printers, and other devices by connecting them together into a local area network (LAN).
- Firewall: A firewall provides a layer of protection between your office network and outside networks, helping keep malicious actors at bay.
- Wireless Access Points: Wireless access points provide Wi-Fi to computers and other equipment on your office network.
- Cables: Cables are used to link all the components of your office network together.
- Network Interface Cards: Network interface cards provide the physical connection between computers and other devices on a LAN.
- Server: Servers provide a central storage location for critical data and applications, as well as allow users on the office network to connect to the internet.
- CCTV Cameras: CCTV cameras can be used for security purposes and to monitor activity in the office.
- EPBX Landline Connection: An EPBX landline connection links your office phone system to a public telephone network.
- IP Phone: An IP phone allows you to make and receive calls via the Internet.
- Scanner & Printer: Scanner and printer are used for document printing and scanning purposes.
- Video Conference Device: A video conference device allows you to hold conferences and meetings remotely.
Network Software Requirements
- Operating System: A network operating system provides the software basis for your office network, enabling communication between computers and other devices on the LAN.
- Network Protocols: Network protocols are used to define the rules of data exchange between computers on a LAN. Commonly used ones include TCP/IP and AppleTalk.
- Firewall Software: Firewall software is used to control the flow of traffic into and out of your office network, helping protect against malicious attacks.
- Network Security Software: Network security software provides additional layers of protection by monitoring, detecting, and responding to threats on your office network.
- Data Storage Solutions: Data storage solutions such as file servers or cloud-based storage are essential for storing and backing up data on your office network.
- Network Monitoring Tool: A network monitoring tool can be used to keep track of network performance and alert you to any potential issues.
- Network Management Tools: Network management tools provide an easy way for administrators to configure, monitor, and manage the devices on their office networks.
How To Set Up An Office Network?
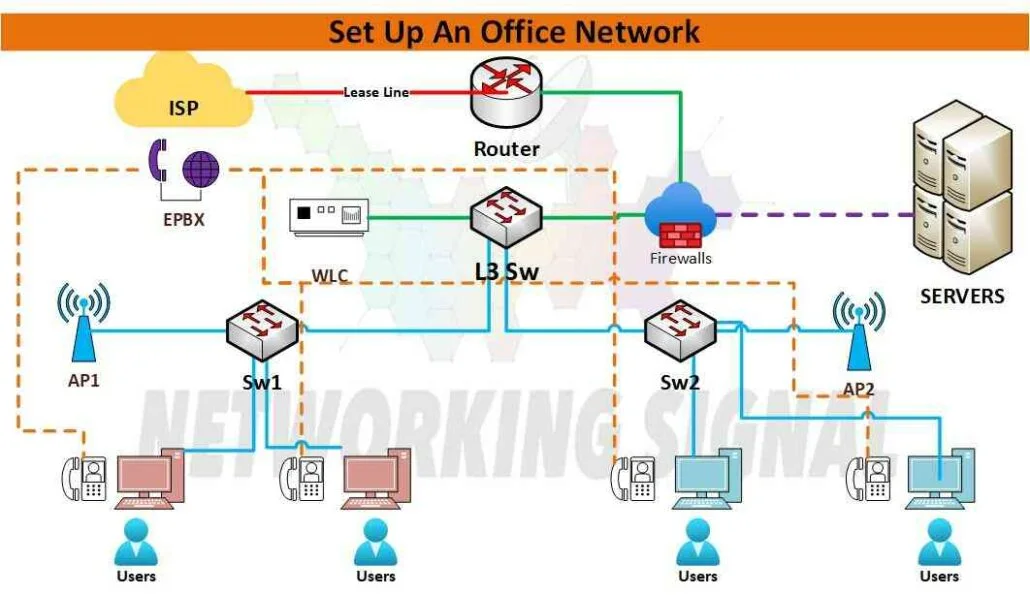
Here are the steps to set up a small office network:
- Install the necessary hardware, such as routers, switches, and access points.
- Connect all devices to the router or switch using cables for wired connections and Wi-Fi for wireless connections.
- Configure network settings such as IP addresses and DNS servers on each device.
- Set up a firewall and configure security settings to protect your office network from malicious threats.
- Install the necessary software such as operating systems, data storage solutions, and network monitoring tools.
- Test the connection speed and performance of your office network to ensure everything is working properly.
- Troubleshoot any issues that may arise and modify settings as needed.
- Monitor the network regularly to ensure everything is working optimally and keep track of any security threats that may arise.
- Make sure your staff is aware of proper network usage, such as not downloading or sharing copyrighted materials or engaging in online activities that could put your office network at risk.
Here is the full detail for setting up a small office network ( For up to 20 Users ).
Select Lease Line Connection
First of all, you need to select a lease line connection from an ISP (Internet Service Provider) for your office network. Depending on the size of your office and the number of users, you may opt for different Internet speeds such as 10 Mbps, 20 Mbps, or higher. The type of connection you select will depend on the budget, usage, and location.
With a leased line, you can get EPBX (electronic private branch exchange) landline connection, IP phone connectivity, and other internet services.
- Example: You can opt for a 20 Mbps EPBX connection with 8 landlines, 10 IP Phones, and 20 Mbps Internet Data Connectivity. This will be suitable for up to 20 users.
Select the Network Hardware
Next, you will need to select the network hardware such as routers, switches, and access points. Depending on the size of your office, you may opt for different models with more features or higher speeds.
In addition to this, you will also need cables for wired connections and Wi-Fi routers for wireless connectivity. You can purchase these from any computer shop or online store.
- Example: You may opt for a 24-Port Gigabit Switch (Cisco Catalyst WS-C2960X-24TS-L), a Router with 4-port Gigabit (Netgear, Cisco), an Access point (TP-Link, Cisco, Google).
Look Here:
Network Hardware Gears
Select Security/CCTV Devices
You will also need to select security devices such as firewalls, antivirus software, and CCTV cameras. The type of security device you select will depend on the size of your office and your budget.
- Example: You may opt for a firewall (Sonicwall TZ400) with Antivirus Software (Avast) and 4 HDCCTV Cameras (Amcrest) for your office.
Look Here:
Security & CCTV Devices
Select Network Cables
You will also need to select the appropriate cables for wired connections. Depending on the type of connection you have, you may opt for Cat5e or Cat6a Ethernet cables.
- Example: If you are using a Gigabit Switch and Router, then you should use Cat6a Ethernet cables as they provide better speeds compared to Cat5e cables.
Look Here:
Network Cables
Select the Server & Printer/Scanner
To complete the setup, you will need a server for hosting applications and services. Depending on your needs, you can opt for a physical server or a virtual one. You may also need to purchase a printer/scanner if required.
- Example: If you want to host an email server with Microsoft Exchange, then you should opt for a physical server such as Dell R620 or HP ProLiant DL380 G9.
Look Here:
Server & Printer/Scanner Devices
After selecting the hardware, you will need to install and configure them.
Installation of Network Hardware
Once you have selected the hardware, you will need to install and configure them. This may involve routing cables from one device to another, setting up switches and routers, installing firewall software, and configuring access points.
- Example: If you are using a Cisco router and switch, then you can use the command-line interface (CLI) to configure them. You can also use a web-based graphical user interface (GUI) to make the process easier.
Configuration of Security/CCTV Devices
After installing the hardware, you will need to configure the security devices such as firewalls and CCTV cameras. This may involve setting up permissions for different users, configuring access points, and setting up motion detection for CCTV cameras.
- Example: If you are using a Cisco firewall, then you can use the rule sets to configure the access permissions. For CCTV cameras, you can set up motion detection and alerts for intrusion or theft.
Installation of Server & Printer/Scanner
Once the hardware is installed and configured, you will need to install and configure the server. This may involve setting up an Active Directory (AD) domain controller, a DNS server, a DHCP server, and a file server.
For Printer & Scanner, setting up local user accounts, configuring sharing settings, installing drivers for the printer/scanner, and configuring network printing.
- Example: If you are using a Windows Server, then you can use Active Directory (AD) to create local user accounts. For printers and scanners, you can install the drivers and configure network printing using a web-based GUI.
Once you have completed these steps, your office network setup is ready to use. You can now access applications and services from any device connected to the network.
How You Can Test The Office Network?
Once the network setup is complete, you can test it on the basis of many parameters.
To Test Performance
- You can use tools such as iPerf, to measure the performance of your network.
- You can also use a ping utility to test the response time and reliability of your network connections.
To Test Security:
- You can use services such as Nessus or OpenVAS to scan for vulnerabilities on your network.
- You can also use a packet sniffer such as Wireshark to detect any malicious traffic on the network.
To Test Bandwidth
- You can use a bandwidth testing tool such as Speedtest to measure the internet connection speed.
- You can also use a tool such as NetLimiter to monitor the data usage of each device on the network.
What network topology is used in offices?
The most common network topology used in offices is a star topology. In this type of network, all the devices are connected to a central hub or switch which acts as the single point of communication between them. This arrangement allows for easy expansion and upgrades since new devices can easily be added to the existing setup.
Another popular topology is a mesh topology where each device is connected to multiple other devices, allowing for redundancy and increased security. This type of setup is more expensive but provides better performance and reliability.
Which type of Network is Good for Office Network?
The best type of network for an office is a Local Area Network (LAN). This type of network provides fast and reliable connections, as well as secure access to data. It also allows users to share resources such as printers, scanners, and other devices.
A LAN can also include different types of networks such as switched Ethernet or wireless networks. Switched Ethernet is the most common type of network used in offices since it offers high-speed data transfer. Wireless networks provide flexibility and convenience, allowing users to access the network from anywhere in the office.
How Does Office Network Set Up Different from Home Network Set Up?
The main difference between an office network setup and a home network setup is in the security measures taken to protect data. Office networks typically use complex passwords, encryption keys, and firewalls to keep unauthorized users from accessing corporate data.
Home networks often use basic or no security measures at all, which can leave them vulnerable to hackers and other malicious activity.
In addition, office networks typically have more complex network topologies than home networks.
Office networks often include multiple routers and switches, while home networks usually have just one or two devices connected to the internet. This allows office networks to handle more users and traffic, as well as provide increased security.